Chukar
General Description
A chunky, medium-sized bird introduced into North America from Eurasia, the Chukar is a pale-colored, but boldly patterned bird. The bird's red bill and legs contrast with its pale gray upperparts. A black line surrounds the bird's whitish throat and cheek, and extends over its eyes. The Chukar's sides are cream with bold black stripes. Pale orange under-tail coverts and red outer feathers adorn its short gray tail.
Habitat
Chukars can be found on steep, dry, rocky slopes with shrub-steppe vegetation. Because cheatgrass is a major food source, Chukars are often spotted near this introduced grass. They survive at elevations ranging from 500 to 4,000 feet.
Behavior
Often found in small groups, especially in the winter, Chukars feed primarily on the ground, but will climb into shrubs or trees for berries.
Diet
In Washington, cheatgrass and wheat seeds make up the majority of the Chukar's diet. In the winter, Chukars feed primarily on seeds, cheatgrass, and thistles, switching to insects and green leaves in the summer. Many of the Chukar's major food sources, like the bird itself, have been introduced from Eurasia.
Nesting
To make the nest, the female creates a depression in the ground and lines it with grass, twigs, and feathers. The nest is typically hidden under a shrub or rock. Clutches are large, with 8-14 eggs that the female incubates. Female Chukars sometimes lay a second clutch of eggs that the male will incubate while she continues to incubate the first. Shortly after hatching, the young leave the nest to find their own food, although one or both parents will continue to tend them for some time.
Migration Status
Permanent resident
Conservation Status
The first Chukars were introduced in North America in 1893 and are still released regularly in Washington. They thrive on overgrazed open ranges where there is no agriculture. Chukars are one of the most popular upland game species in Washington, ranking second in the state for numbers harvested. Chukars typically exist in areas unoccupied by other upland birds, thus their introduction does not interfere with native species.
When and Where to Find in Washington
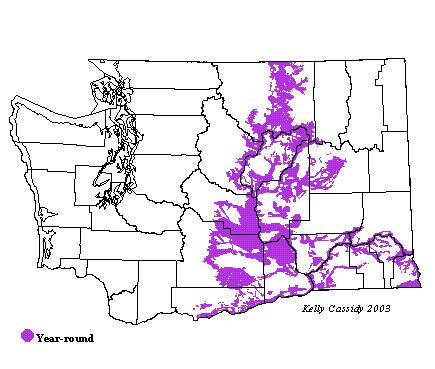
Chukars are regularly released to provide opportunities for hunters and thus are often seen outside their regular range. They are common in rocky, shrub-steppe areas and deep river canyons east of the Cascades in the central and lower Columbia Basin. They can be found along the Columbia River in Klickitat County, and in the Methow and Okanogan Valleys, in the Banks Lake area, along the lower Yakima River and tributaries, and along the eastern portion of the Snake River.
 Abundance
Abundance
| Ecoregion | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oceanic | ||||||||||||
| Pacific Northwest Coast | ||||||||||||
| Puget Trough | ||||||||||||
| North Cascades | ||||||||||||
| West Cascades | ||||||||||||
| East Cascades | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | U |
| Okanogan | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | U |
| Canadian Rockies | ||||||||||||
| Blue Mountains | F | F | F | F | F | F | F | F | F | F | F | F |
| Columbia Plateau | F | F | F | F | F | F | F | F | F | F | F | F |
Washington Range Map
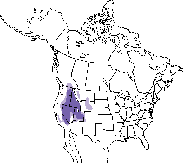
North American Range Map

Family Members
 ChukarAlectoris chukar
ChukarAlectoris chukar Gray PartridgePerdix perdix
Gray PartridgePerdix perdix Ring-necked PheasantPhasianus colchicus
Ring-necked PheasantPhasianus colchicus Ruffed GrouseBonasa umbellus
Ruffed GrouseBonasa umbellus Greater Sage-GrouseCentrocercus urophasianus
Greater Sage-GrouseCentrocercus urophasianus Spruce GrouseFalcipennis canadensis
Spruce GrouseFalcipennis canadensis White-tailed PtarmiganLagopus leucura
White-tailed PtarmiganLagopus leucura Dusky GrouseDendragapus obscurus
Dusky GrouseDendragapus obscurus Sooty GrouseDendragapus fuliginosus
Sooty GrouseDendragapus fuliginosus Sharp-tailed GrouseTympanuchus phasianellus
Sharp-tailed GrouseTympanuchus phasianellus Wild TurkeyMeleagris gallopavo
Wild TurkeyMeleagris gallopavo

